ERYTHROCYTES:
POSITIVE VISUAL
IDENTIFICATION
Clifford E Carnicom
May 03 2001
Positive visual identification of erythrocytes, or red blood cells, is now apparent from the microphotographs which are presented on this page. The samples shown are taken from atmospheric testing in Santa Fe, NM using the methods of electrostatic precipitation as described earlier.
The bi-concave surfaces, circular shapes, and dimensions of the structures shown are an indisputable match with that of erythrocytes. Professionals, citizens, activists and researchers are requested to conduct these tests independently for verification or refutation of what has been repeatedly presented through recent atmospheric analysis.
The magnification achieved on this most recent analysis makes the case quite clearly that biological components are now a regular feature of the atmosphere that we all breathe. This is in addition to the saturated level of particulate matter that has been documented at an equal level of veracity, along with the obvious degradation in visibility that is now all too apparent. Crimes of the highest order are being perpetrated on the citizens without their knowledge or consent. The citizens of this country must confront this issue in a public and vocal forum with urgency.
Any positive refutation of the results shown on this page by any responsible party will be immediately presented. Any refutation will require a duplication of the collection and analysis methods that have been employed. Sincere and genuine efforts to examine these findings in an honest fashion is invited and encouraged.
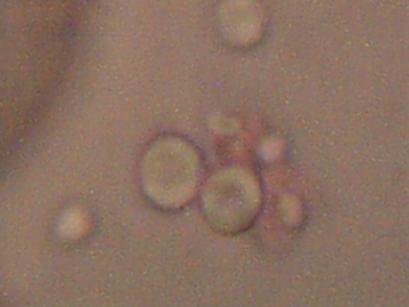
Magnification approx. 5000x
Bi-concavity characteristic of erythrocytes readily visible.
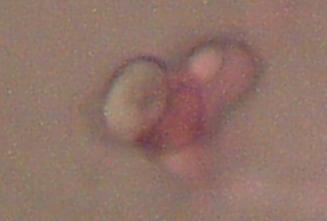
Magnification approx. 5000x
Bi-concavity characteristic of erythrocytes readily visible.
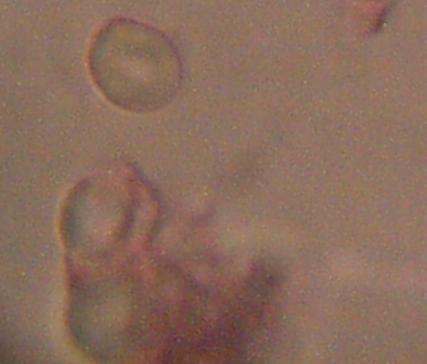
Magnification approx. 5000x
Bi-concavity characteristic of erythrocytes readily visible.
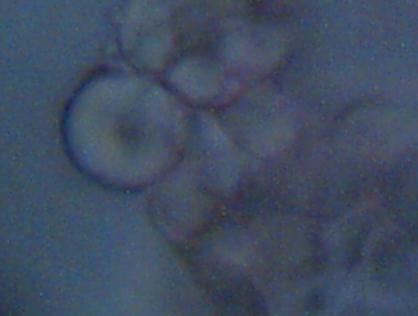
Magnification approx. 5000x
Bi-concavity characteristic of erythrocytes readily visible.
Specifics of collection in this case are as follows:
Samples are collected by electrostatic precipitation as described earlier. Air volume also exposed to a humidifier during processing to enhance aggregation. Samples collected on clean microscope slides. Wet mount slides using eosin stain prepared prior to digital image collection. Dessication appears to remain a viable consideration, as some cells appeared to reconstitute to a degree from the eosin stain. Degradation of the cell structure appears to occur over extended exposure to this particular stain. Images viewed with an immersion oil objective at 1000x, and joined with a digital coupler to achieve a magnification of approximately 5000x. Results are in complete agreement and concordance with previous analyses at lower levels of magnification using both electrostatic precipitation and HEPA filter techniques. Size of the cells measure from 4 to 7 microns.
Any corrections or revisions to the information presented here will be made as is appropriate.
Clifford E Carnicom
May 03 2001


