Simple Observations, Important Conclusions
by
Clifford E Carnicom
Jul 06 2019
What follows below completes a loop of an important branch of research that has taken place at Carnicom Institute throughout this last decade.
The images below will demonstrate that an exact match exists between the microbiology of the “Morgellons” condition BOTH internal and external to the body. It also, once again, confirms the studies that confirm and prove that this health condition is in no way limited to skin effects or symptoms.
The Morgellons conditions is the result of very specific and unique microbiology. The characteristics of that microbiology have been studied in great detail and sufficient information to establish and confirm this claim of uniqueness exists on this site. The presentation in the paper “Cross-Domain Bacteria Isolation” (May, 2014) solidifies that claim in the evolution of research. The provisional term, “cross-domain bacteria”, is henceforth referred to as CDB in this and other papers.
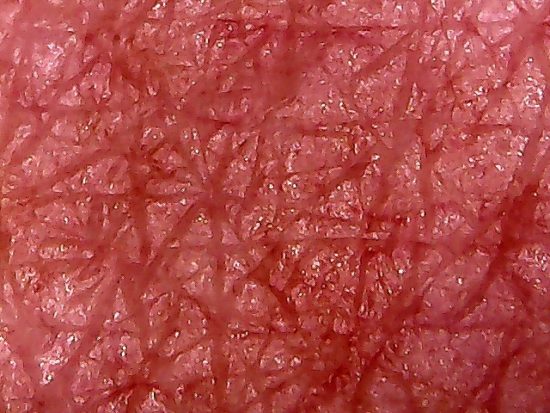 Control Photograph – Normal Skin
Control Photograph – Normal Skin
No skin blemishes visible or apparent.
Magnification approximately 15x.
Further uniqueness of this microbiology has been established in the recent published paper, “The Evidence is Evident” (Jun 2109). All comments within that research paper apply equally toward the information that is presented here, and it would be apropos to be equally familiar with that previous work.
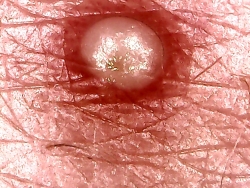
The following two images depict a type of skin anomaly that presents itself within the “Morgellons” conditon. These can exist at numerous locations on the body, and they are strongly irritating. In the case shown here, the disturbance is small and not readily visible to the naked eye.
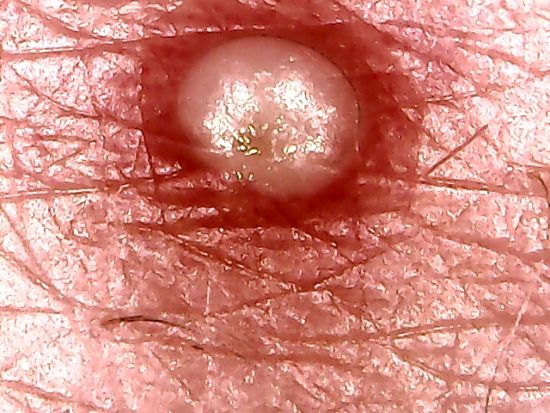
Microphotograph of a skin blemish from an individual that
displays symptoms characteristic of the Morgellons condition
Magnification approx. 15x.
The skin disturbance shown above was opened slightly to retrieve a small exudate sample for observation under the microscope.
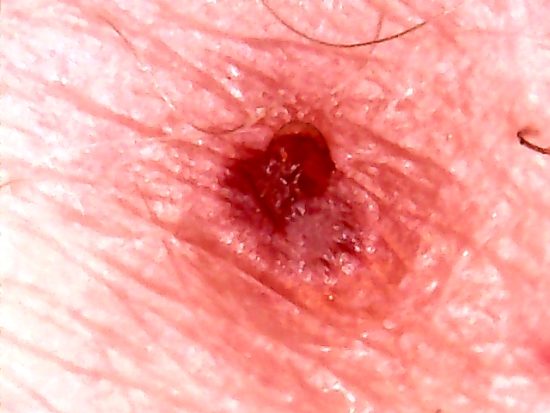
Microphotograph of blemish that has been opened to remove exudate .
This image is from an individual that exhibits external symptoms
of skin conditions that are characteristic of the Morgellons condition.
Magnification approx. 15x.
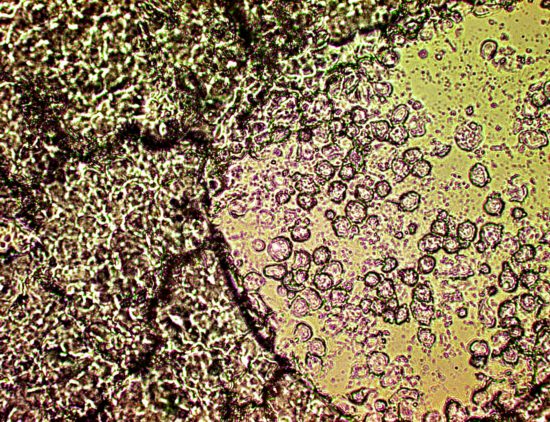
A microscopic view of the skin exudate at moderate magnification.
No special detail is evident here, however, signs of a filamentous
composition can be observed in the left side of the photograph.
In addition, cellular structures with signs of disruption can be seen
in the right half of the photographs. No signfiicant conclusions
regarding detailed structure or variation can be determined at
this level. Magnification approx. 3200x.
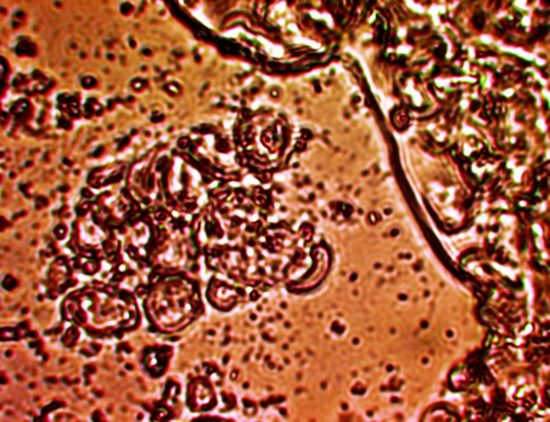
A microscopic view of the exudate at high magnification. Due to the small size
of the CDB (approx 0.3 micron), this higher level view is required to extract the detail
necessary to assess the internal structure of the exudate. The assessment
is that numerous damaged or broken erythrocytes (red blood cells) from
the exudate are infused with large numbers of the CDB microbe.
The filament structures that accompany the CDB microbial growth
are also more readily visible. Magnification approx. 8000x.
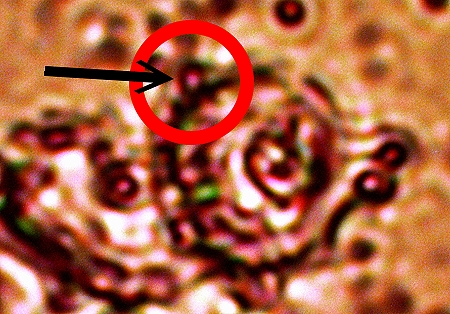
Closeup view of individual CDB within disrupted erythrocyte
representative of skin exudate. Size of CDB is approx. 0.3 micron.
Original magnification approx. 8000x.
The microscopic observations above bring to immediate recall an earlier analysis made approximately one decade ago in a research paper titled, “A Mechanism of Blood Damage” (Dec, 2009)
__________________________________
The introductory statement made at the time of that paper was as follows (Dec 14, 2009):
“An organism and a method that damages the condition of the blood has now been identified and it has been directly observed. The blood variations reported here are in direct association with the existence of and the severity of the so-called “Morgellons” condition.”
__________________________________
We are therefore at a point, approximately a decade later, to assertively claim that what is exuded through the skin of those affected by the Morgellons condition is an exact microbiological match to that which is known to exist within the blood and body fluids of those affected by this same condition. This microbiology is now well established, and is no longer subject to ambiguous debate. Readers are once again referred to the recent paper “The Evidence is Evident” for additional substantiation of these facts.
We shall now recall a couple of the images of affected blood that were presented close to one decade ago within the reference paper cited above, “A Mechanism of Blood Damage”.
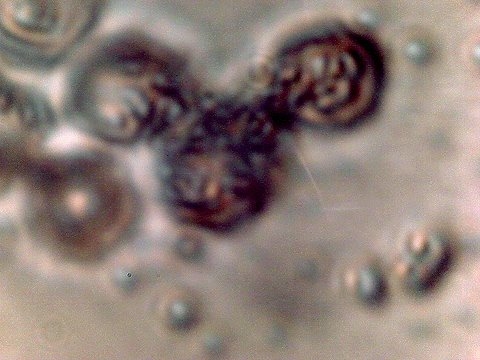 Magnification of highly degraded erythrocytes (red blood cells)
Magnification of highly degraded erythrocytes (red blood cells)
heavily infused with the CDB microbe. The blood shown here is veinous
and comes from internal to the body. This image was reported
in Dec. of 2009. The structural details of microbial damage in this case
match exactly the form, style and method of erythrocytic damage
shown in this current report. Magnification approx. 7000x.
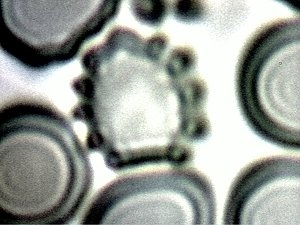
Erythrocytes (red blood cells) in the process of degradation
by the CDB microbe. The blood shown here is capillary and comes from internal to
the body. This image shows an earlier stage in the evolution of damage to the cells,
as reported in the “A Mechanism of Damage” paper. This image was reported in
Dec. of 2009. Magnification approx. 10,000x.
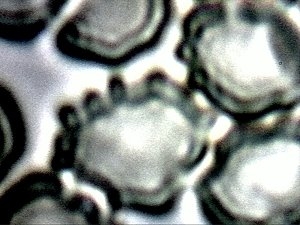
Additional image of earlier stages of degradation of erythrocyte by the CDB,
as reported in 2009. Magnification approx. 10,000x.
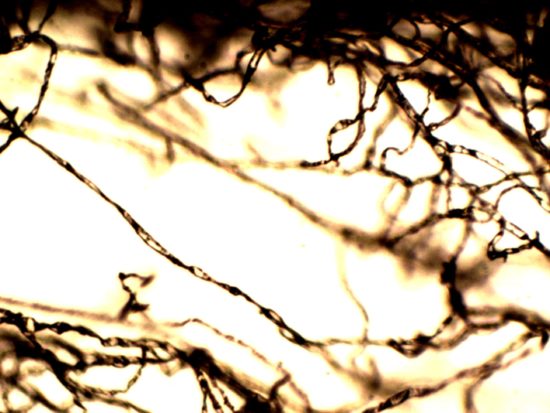

To further demonstrate the co-existence of filamentous growth and its origin
from the CDB, these images show filaments that are also know to be characteristic
of the Morgellons condition. The filament structures here were exuded from the
same individudal that provided the skin exudate samples of this current report.
These filaments developed in hair-covered portions of the body, and they were
collected approximately six months prior to this report.
Moderate magnification (~ 800 – 1200x)
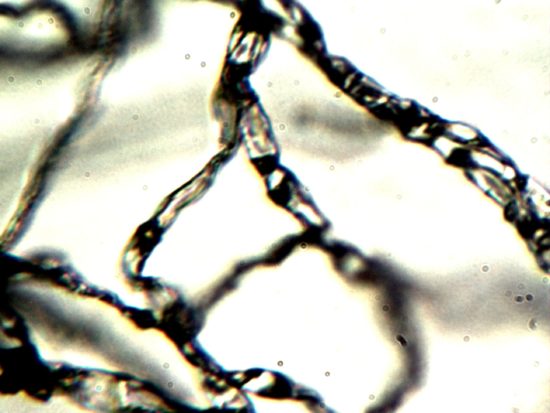
An additional microphotograph of the filamentous growth
from the skin of the affected individual.
Higher magnification (~ 2000 – 500x)
The definitive findings of the microbiological origin and nature of the Morgellons condition (i.e., CDB) are ultimately to be recognized and acknowledged by the scientific and health communities. The research is established to the point where avoidance and/or obfuscation is no longer permissible or acceptable. Those that are able to act independently often are more receptive, flexible, and progressive with such change. Governments are likely to be the slowest to follow suit. If the motive to improve the state of our well-being exists, significant financial infusions will be required. The pace of that acknowledgement and acceptance is a process that we are all, inevitably, involved with.
Clifford E Carnicom
Jul 06, 2019
_____________________________________________
Additional note: Near infrared (NIR) scans of affected skin areas and of control normal skin have been collected to further establish the microbial signature of the Morgellons condition.