ION STATUS REPORT
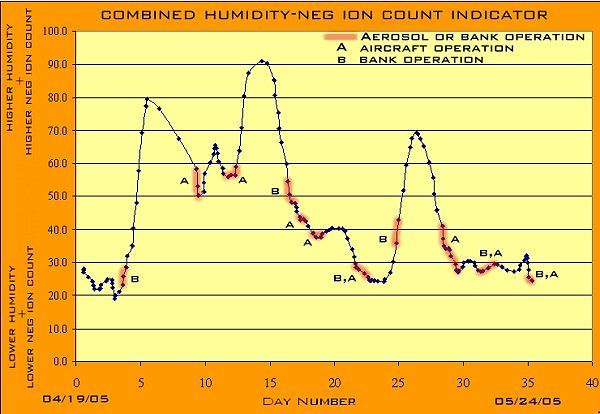
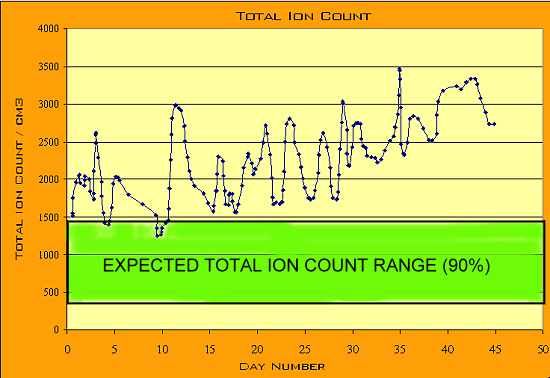
A graph showing the ion count, based on a direct measurement by Clifford Carnicom over a 47 day period (April 1, 2005 to June 19, 2005) in Santa Fe, New Mexico is the object of this page. This graph shows an increasing ion count over the timeframe described. Readers may wish to visit the previous Carnicom paper titled ’IONS & HUMIDITY’ (dated May 26, 2005) for more information on this topic and the graph’s interpretations.