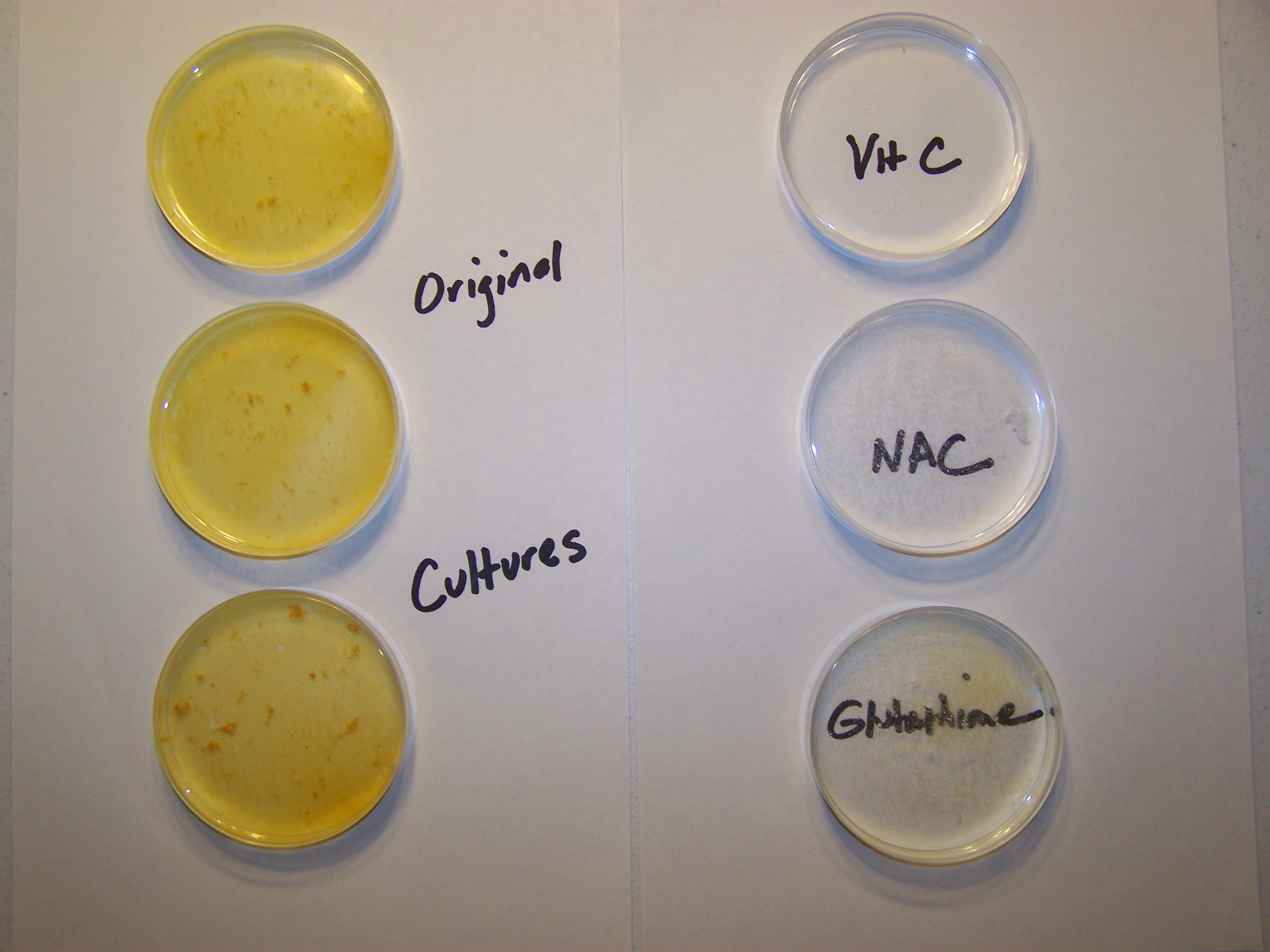
Growth Inhibition Achieved
Inhibition of growth of the so-called "Morgellons" condition in a cultured environment has been achieved. The primary agents of reduction here, both literally and chemically, are a series of powerful antioxidants. These include ascorbic acid (vitamin C), N-Acetyl Cysteine (NAC) and glutathione. The photograph below shows the result of a culturing process which has been subjected to these antioxidants and their impact upon growth; the effects are rapid and repeatable. The source of this culture is the result of a series of incubation, collection, isolation, extraction and purification processes applied to previous cultures. The original cultures are based upon the use of a variety of human, animal and plant samples, each of which produces identical growth forms. One of many precedents for this work is contained within a previous paper entitled, "Morgellons : A Discovery and A Proposal" (Feb 2010). The basis of the current work is a significant advancement in the development of culture methods.