MORGELLONS: GROWTH CAPTURED
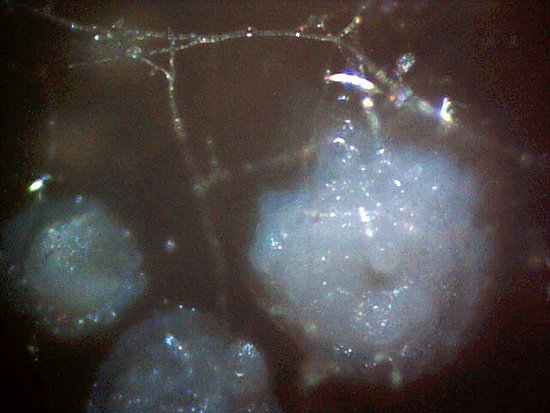
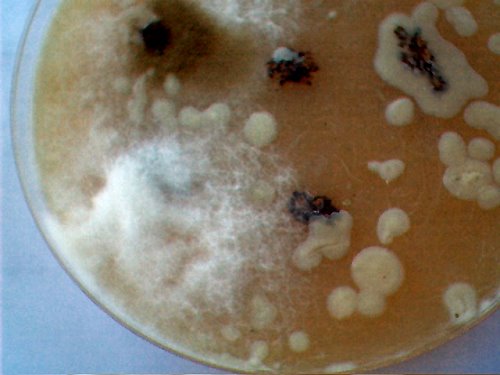
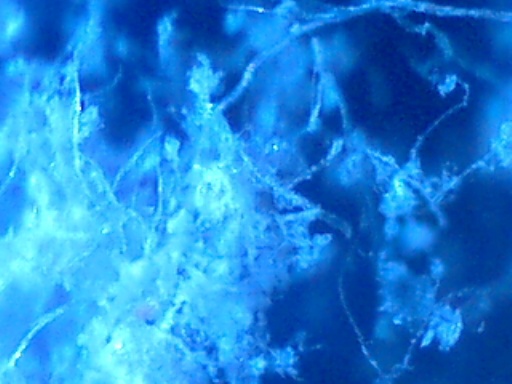
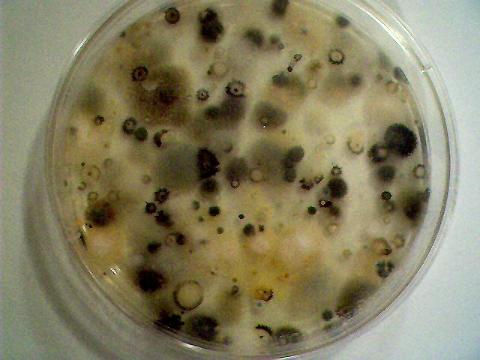
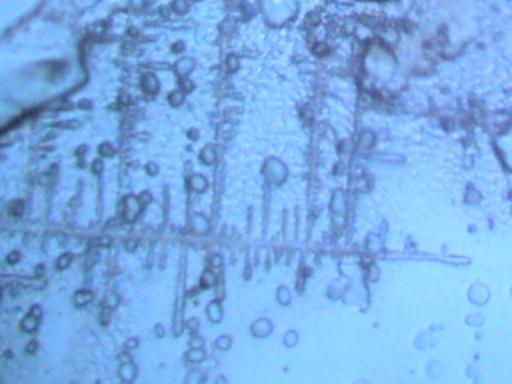
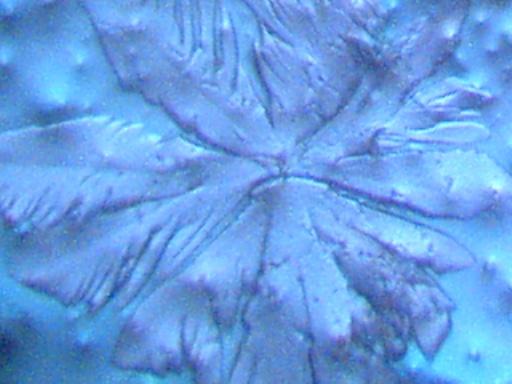
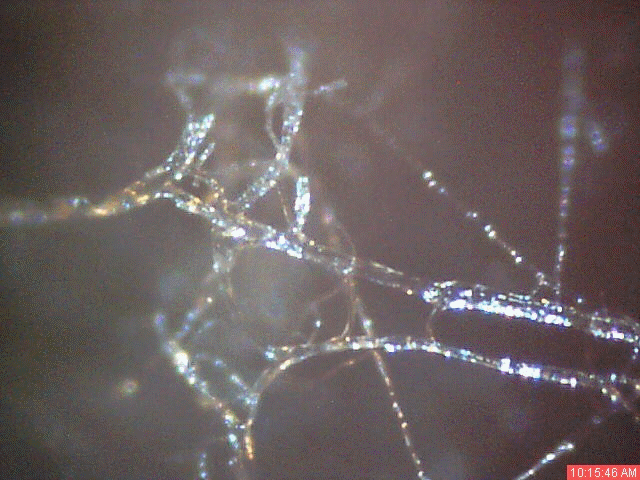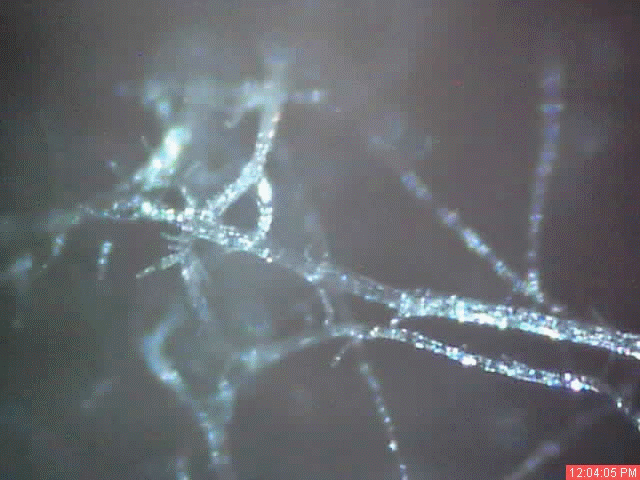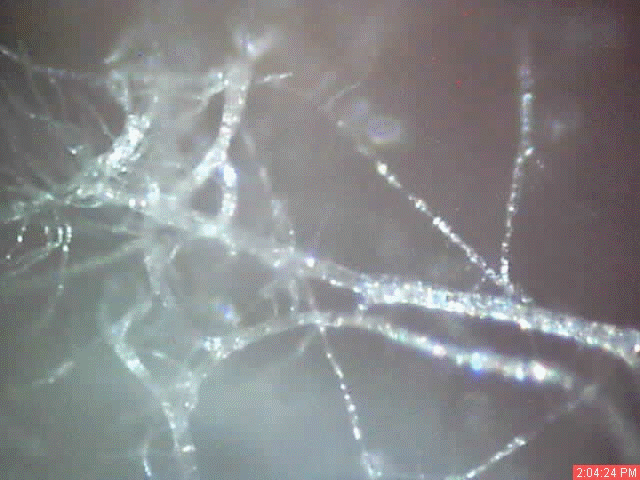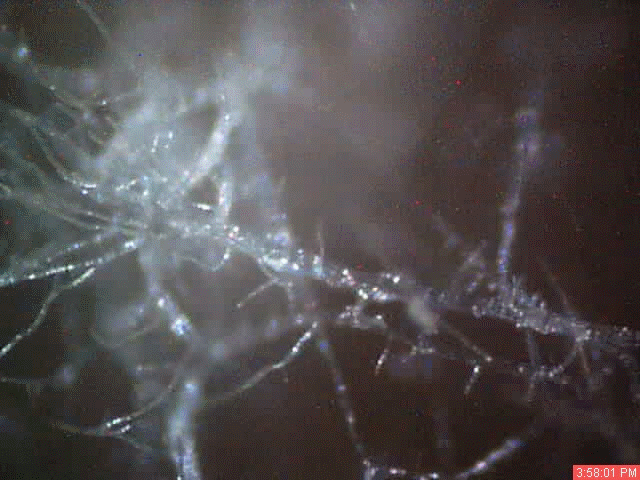
A time lapse video under the microscope has been developed and presented on this page which demonstrates the cultured growth pattern and behavior of a primary pathogenic form that is in direct association with the so-called "Morgellons" condition. The time lapse video covers a period of approximately six hours and compresses the time into approximately one minute with 30 frames. From the discovery shown here, it would appear that the encasing filament serves to provide feeder or extension filaments which serve to extend the growth of the pathogen. The estimated growth rate of the extension filaments on this particular culture is on the order of 50 microns per hour, or roughly the width of a thin human hair per hour. This report continues to add valuable knowledge on the morphology, characteristics and behavior of at least some of the pathogenic forms that are strongly associated with the so-called "Morgellons" condition.