DECELERATION CONTINUES
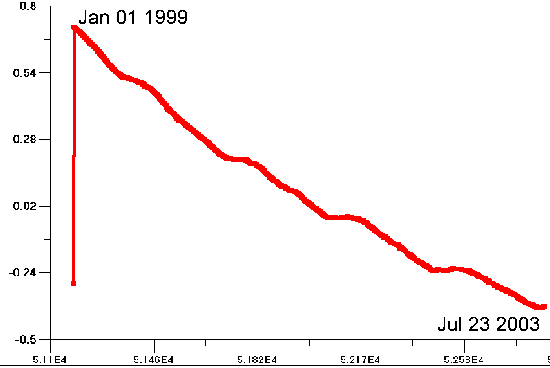
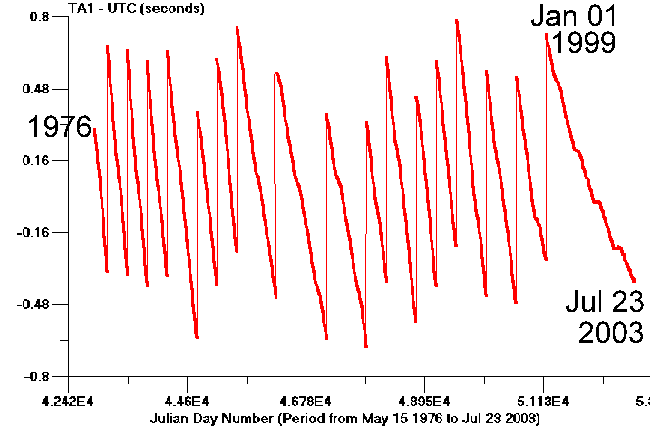
A detailed statistical analysis of time over a period of four months presented in this paper continues to support the hypothesis of an earth in a state of deceleration. The magnitude of the deceleration, if confirmed, is sufficient to anticipate unusual geophysical activity in the foreseeable future. Small changes in time will translate to large changes in the kinetic energy of the earth. One second of time change per year corresponds roughly to the energy contained within all of the fossil fuels of the earth. The magnitude of the deceleration is currently best estimated at approximately 0.3 milliseconds per day. Any deceleration component of rotation of the earth is to be regarded with the greatest of interest, as an apparent small acceleration (deceleration) will result in significant velocity differentials and accumulated time differentials over a relatively short period of time if sustained. A deceleration component of 0.3 milliseconds per day will result in a velocity change of approximately 0.1 seconds per day at the end of a one year period. This same deceleration component would lead to an accumulated difference of approximately 20 seconds of time after a one year period. These are phenomenal magnitudes relative to any historical basis that is available.