A Source of Global Harm: The Cross Domain Bacteria (CDB) Proteins
Sep 02 2023
Clifford E Carnicom
The assessment by Carnicom Institute (CI) is that the proteins created by the Cross Domain Bacteria (CDB), a subject of extended study here, are responsible for a vast majority of the health ills imposed upon the global population, including the more recent tragedies involving blood coagulation and clotting of the “Covid Era”.
The starter for the cultures is human blood. Culturing of this biological entity has a long history within CI. One major advantage of the culturing process is that it allows for the study of biological growth (synthetic or otherwise, as the case may be) in a controlled environment. This provides for many studies and discoveries that would simply be impossible otherwise. Recent advances and refinements in CDB culture practices have been used to isolate four separate proteins from this organism; this has major ramifications for human health now and in the future.

One of Four Protein Forms Isolated From CDB Cultures
This paper will simply establish the existence of the various protein forms, along with a brief discussion of their character. These proteins serve as a window to great understanding of what has transpired, what is currently happening, and what will continue to degrade human health and threaten existence unless “engagement” (as mentioned in the previous paper, The Source of Blood Coagulation: Cross Domain Bacteria (CDB)) commences at the highest level possible. The broader demands and requirements here far exceed the capabilities of CI.
A logical step in biological discovery begins with DNA analysis. Even the nomenclature given to this microorganism by necessity, and not desire, depends upon this initial information. The biological and genetic origin of this entity remains unknown, but the properties of its existence force upon us the issue of synthetic biology. Until that DNA information is acquired at a minimum to the “domain” level, we will remain in ambiguity. CI has successfully isolated DNA from this organism on three occasions over the decades.
Let it be disclosed at this time, however, that good faith efforts were made by CI to seek out this preliminary DNA analysis several years ago. Professional services were consulted and appropriate requests were made to seek domain level DNA identification. Those requests were denied with no rational or just cause from a scientific standpoint. It is fair to say that certain “filters” seemed to be operative within the discussions that took place, and that those filters established a wall that has kept the populace in ignorance ever since. The atmosphere and tone of that meeting had similarities to those written years ago in the paper, Environmental Filament: False Lab Report (Jan 2013); this may also be of interest.
After DNA comes protein, which is where we are today. Proteins are the most abundant constituent of living organisms after water. They offer the most meaningful insight into the nature of biological existence. The same high level of laboratory expertise and resources are required for protein analysis as they are for DNA.
Nevertheless, despite obstruction or limitations, let us put our foot forward and begin to show what is available as a path of understanding in the future. The photos shown here are the evolution of decades of research. With this background, it still requires a couple of weeks of steady work to produce these results. The identification and separation of proteins of a living organism is not a trivial matter. This was also the case for DNA isolation along that same path.
Each of these proteins will be present in the human body if the CDB are present in the body. Thus far, there is no known exception in any observed case, although there is variability in the impact to human health. The focus of the CDB studies within CI research has been human blood, although all body systems show serious detriment. The Morgellons Research Project (Nov 2016) of CI will enumerate the problems in more detail.
A very few generalized comments will be made about each isolated protein.

CDB Isolated Protein No. 1
Protein No. 1 is a water soluble protein. Water solubility of a protein has major implications of distribution within a biological system. Given that more than 3/4 of the human body is water, it is not difficult to envision the prospects for harm from a foreign protein. The CI toxicology studies (numerous research papers 2017-2019) are directly associated with this particular protein form. All indications are that this protein is primarily of polymeric form, and it has a film or “liquid plastic” texture to it upon increased evaporation or drying.

CDB Isolated Protein No. 2
CDB Protein No. 2 varies in solubility depending upon the pH. The solid form of the protein is shown after precipitation is induced from an increase in alkalinity. The consistency of this protein is that of an adhesive paste upon evaporation or drying. Indications are that this protein is also of a polymeric nature.

CDB Isolated Proteins No. 1 & 2 Combined
Protein Nos. 1 & 2 originally coexist in the culture solution. This photo shows both both forms after precipitation is induced for Protein No. 2 causing it to settle at the bottom of the solution.

CDB Isolated Protein No. 3
Protein No. 3 is a solid protein that settles out of culture. The protein has a paste like consistency upon evaporation and concentration. Polymeric aspects of this protein remain uninvestigated at this time.

CDB Isolated Protein No. 4
Protein form No. 4 has been extensively examined over the years at CI. The earliest culture work generated this form and extensive research on that work is available on the CI site. The long history of equivalency between the “Environmental Filament”, human biological study (under the colloquial identity of “Morgellons”), and culture results is documented in excruciating detail on the CI site. The filament structure, especially as this protein form is known to share equivalency with the “Environmental Filament” of CI research, also strongly implicates polymeric formation.
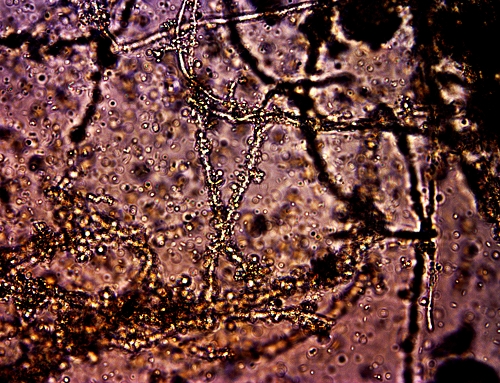
CDB Isolated Protein No. 4 Under the Microscope
CDB in Large Numbers Enmeshed within Filament Network
Magnification 3200x
Above is a microscopic view of the filament protein form from the culture. This form is the most heavily observed and documented over the years. The additional proteins now identified from this most recent work provide a pathway to much greater understanding of how human health is impacted by the CDB.

Near Infrared (NIR) Plot of the Set of Four CDB Isolated Proteins
Initial NIR data for the four protein types has been acquired.
Future work will seek more detailed information on the chemical nature of the various proteins so that coarse and early stage biochemical interpretation can be made. This CI work, to the degree possible, will establish further connections between the environmental sciences, human biology, and the impact of the Covid Era. Potential further mitigation strategies, beyond those already discussed, will be explored or proposed. Without the greater “engagement” referred to earlier, this work will be a long term venture with limited accomplishment relative to what is required. Time is not in our favor (and never was) and the humans species does exist under an increased threat of extinction. Transformation of the species, which may ultimately be equivalent to extinction, exists as an additional alternative.



