Growth Inhibition Achieved
Clifford E Carnicom
January 31 2014
|
Note: I am not offering any medical advice or diagnosis with the presentation of this information. I am acting solely as an independent researcher providing the results of extended observation and analysis of unusual biological conditions that are evident. Each individual must work with their own health professional to establish any appropriate course of action and any health related comments in this paper are solely for informational purposes and they are from my own perspective. |
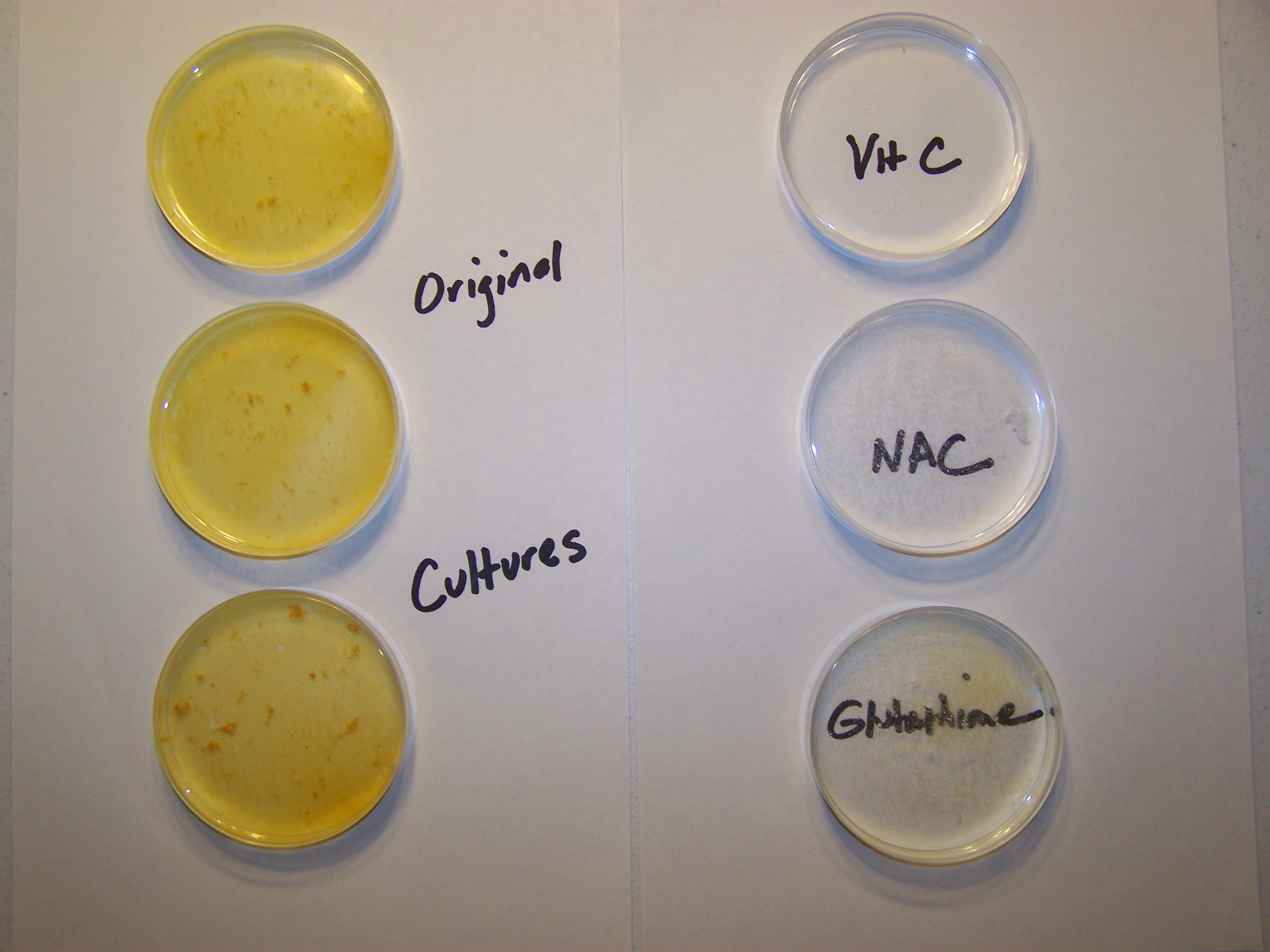
Inhibition of growth of the so-called “Morgellons” condition in a cultured environment has been achieved. The primary agents of reduction here, both literally and chemically, are a series of powerful antioxidants. These include ascorbic acid (vitamin C), N-Acetyl Cysteine (NAC) and glutathione. The photograph below shows the result of a culturing process which has been subjected to these antioxidants and their impact upon growth; the effects are rapid and repeatable. The source of this culture is the result of a series of incubation, collection, isolation, extraction and purification processes applied to previous cultures. The original cultures are based upon the use of a variety of human, animal and plant samples, each of which produces identical growth forms. One of many precedents for this work is contained within a previous paper entitled, “Morgellons : A Discovery and A Proposal” (Feb 2010). The basis of the current work is a significant advancement in the development of culture methods.
At the heart of this “condition”, from the perspective of this researcher, is the presence of a sub-micron cross-domain bacteria that is extremely resistant to extinction. This postulated bacteria has the property of developing the growth of an enclosing sheath, or filament which further serves to house, protect and transport these same bacteria. This sheath, or enclosing filament, also exists in its most primitive form at the sub-micron level. This protective and resilient sheath appears to be composed largely of a keratin (protein) construct, but it also remains impervious and inpenetrable in comparison to other keratin structures such as hair. It is also known that iron is a core constituent of the bacteria composition, as well as amino acids. A more detailed analysis of the organic nature of the life form is available and has been presented within the paper, “Morgellons – A Working Hypothesis” (Dec 2013). Additional important health considerations and strategies are integrated within that paper, and the issue of antioxidants are one of many central themes presented therein. Readers are seriously advised to become familiar with that work; many equally important issues beyond that of oxidative stress are discussed in detail there.
DNA from this life form has been isolated and it exists as a priority of research for Carnicom Institute; please see the paper, “DNA Isolated” (Jan 2014).
It has been stated that the term “Morgellons” is completely insufficient to describe the nature of this life form and its ubiquity in the environment and biology of the planet. The scientific community will be forced to address this deficiency in our future and adequate nomenclature will need to be developed. Ubiquity within biological domains and permanence of existence, even under adverse conditions, will be central to the more complete and scientific characterization and understanding of the life form. Please refer to the paper entitled, “The New Biology” (Jan 2014).
|
A comparison of the original culture growth with the same growth subjected to a series of powerful antioxidants : ascorbic acid, N-acetyl cysteine, and glutathione. The culture growth and treatments span a period of approximately 18 hours. The early stage of culture growth is dominated by a rapid increase in the growth of the bacteria-like form; the filament sheaths represent a more advanced stage of growth to come later in the process. The culture mediums are composed of water, carbohydrates (fructose) and a chelated metal complex that includes iron, manganese and zinc. The culturing methods are rapid and repeatable and they eventually lead to DNA extraction and isolation. One primary mechanism at work in the effectiveness of the antioxidants is the reduction of iron complexes (specifically, ferric to ferrous) within the bacteria. |
Note : It is recommended that citizens and the public copy, duplicate and mirror this site in its entirety in multiple instances (both online and offline) to assist in the distribution and disclosure of the information contained within. There are indications of access and distribution filtering systems that may be in place. Your efforts and attention toward creating a network of permanent history, access and record are appreciated on behalf of the public interest and welfare.
Clifford E Carnicom , Jan 31, 2014
(Born Clifford Bruce Stewart, Jan 19, 1953)