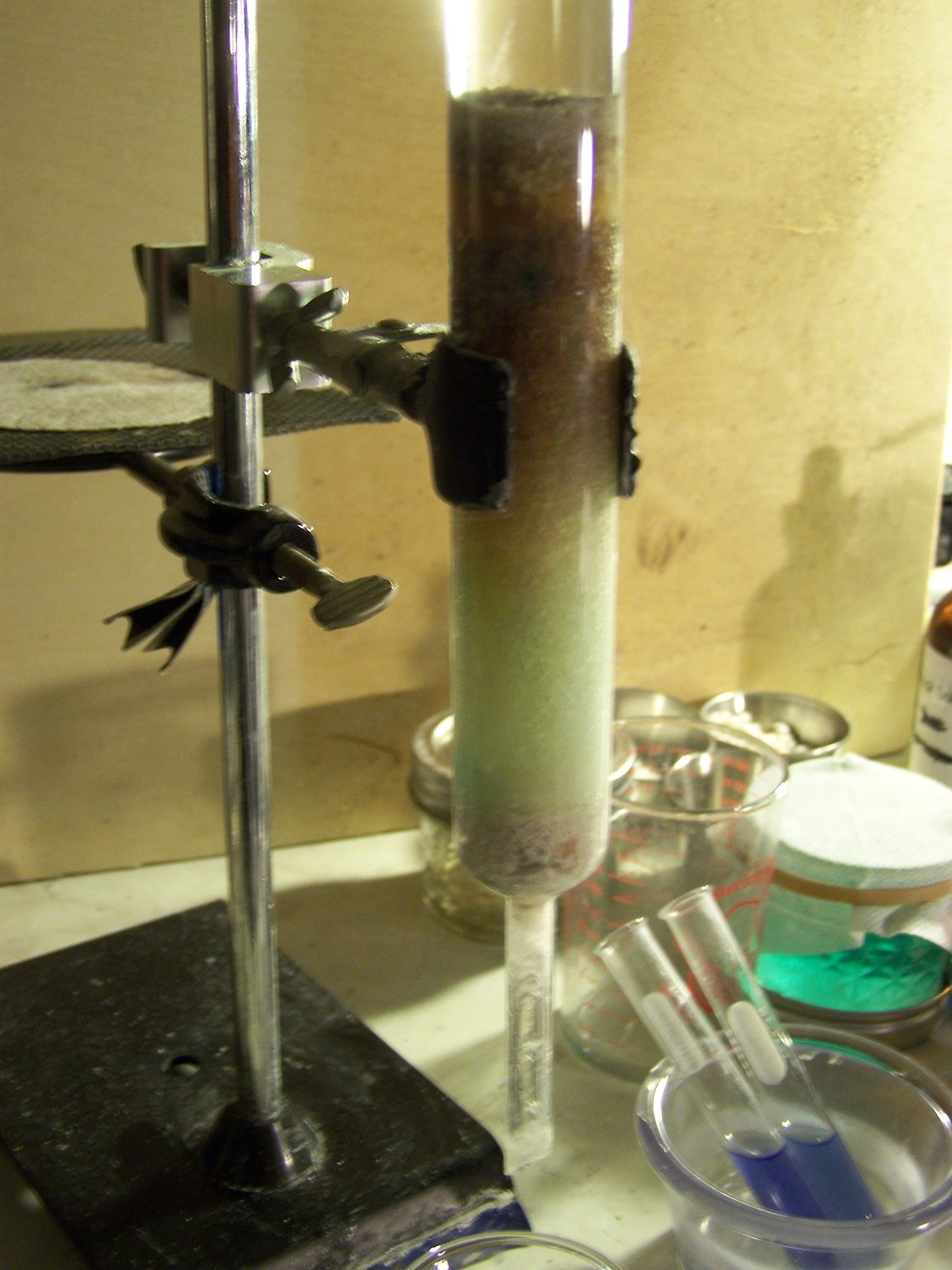
A laboratory analysis of a rainwater sample from a rural location in the midwestern U.S. has been received by Clifford Carnicom, and reveals extremely high levels of potassium and calcium within the sample. Examination of the aerosol issue has, almost from the beginning, focused on the important properties of such elements of Groups I and II of the periodic table. The attention has arisen because of the ease by which such elements are ionized. This ionization will take place in the majority of cases quite readily with the energy available from ultra-violet light and, in some cases, from visible light alone. Candidates for further and future testing, include strontium, aluminum and titanium. A partial list of the effects of ion disturbances upon human health are discussed in this work, and include Impairment of the body's ability to absorb oxygen, the development of allergies, high levels of serotonin in the bloodstream, and a reduction in the body's ability to filter airborne contaminants from lung tissue. Direct research from this site alone now documents unexpected levels of calcium, magnesium, potassium and barium. The acquisition of an ion counter will be a valuable instrument to further this research; if anyone is in a position to provide or loan this device please feel free to contact Clifford Carnicom.