THE THEFT OF SUNLIGHT
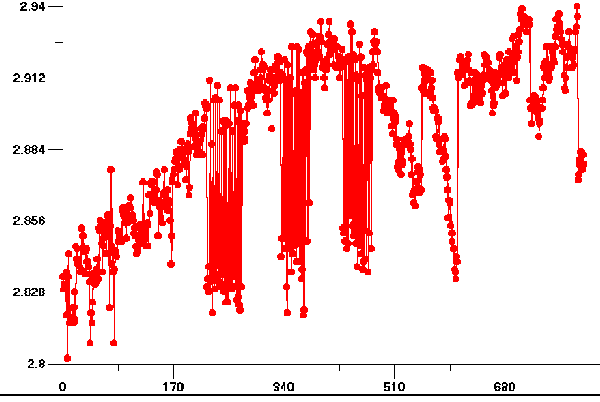
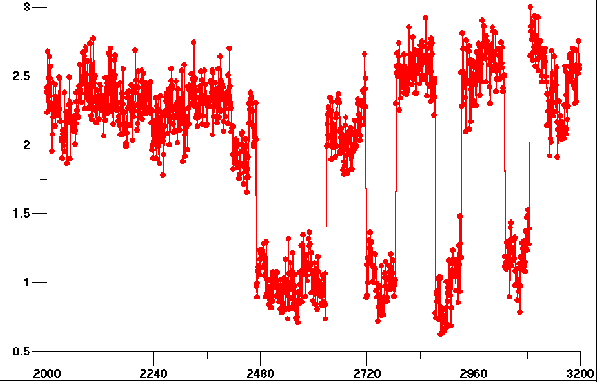
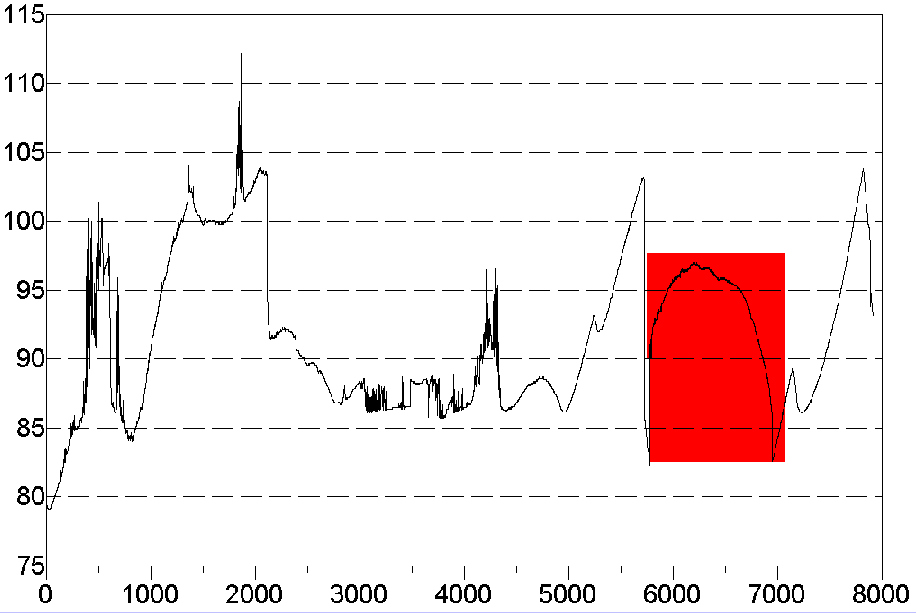
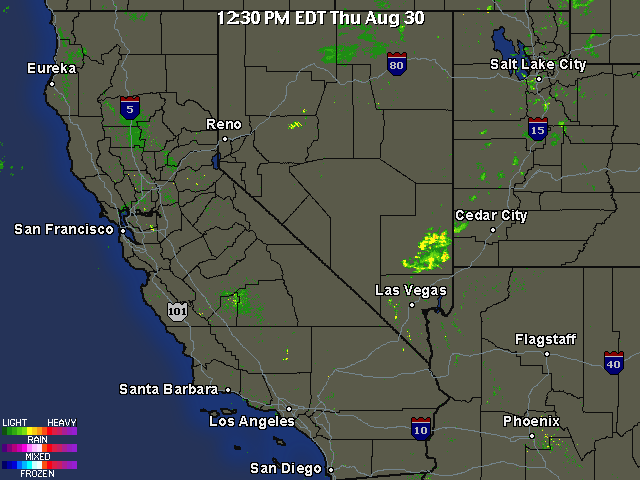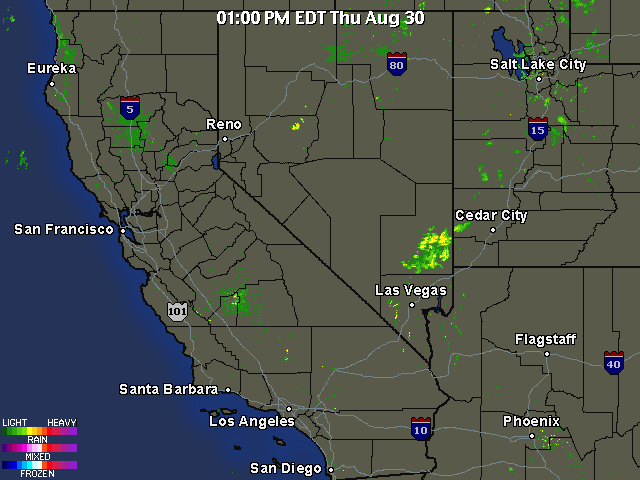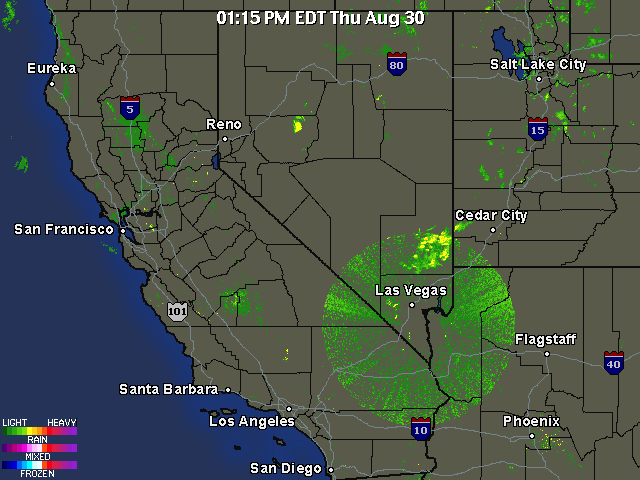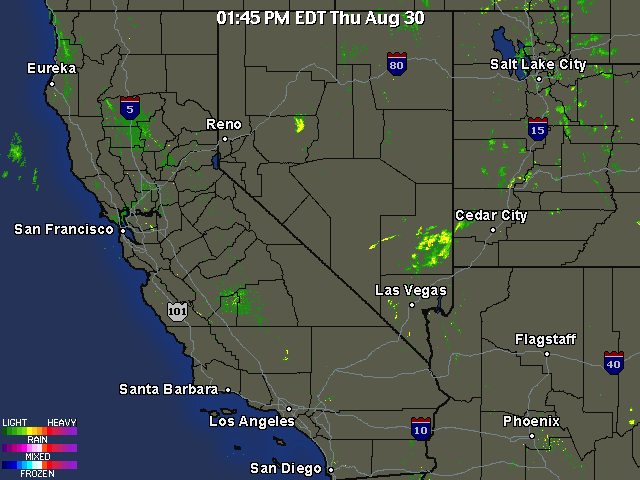
This is a discussion about measurements recently taken with a calibrated photometer that measure the reduction in intensity of sunlight that occurs as a direct result of heavy aerosol operations. These measurements expose a rapid reduction in the transmission of sunlight coinciding with photographs presented on this page that show the aircraft aerosol trails systematically increasing the extent of the aerosol bank.
Interesting to note, is that rather than reducing the temperature of the earth and lower atmosphere, the aerosol operations commonly have the opposite effect of increasing temperature and aggravating, if not inducing drought conditions. This is a result of a combination of factors, including the specific heats of the elements involved as well as the hygroscopic properties of the aerosols. Physical and chemical analysis of the aerosol dynamics will lead to the expected observations of increased temperature, decreased moisture and an increase in winds.